Table of Contents
Usage
Note: the bellow guide applies to versions 2.3 or later. If you're looking for the older usage guide, please read the old version of this page.
Installation
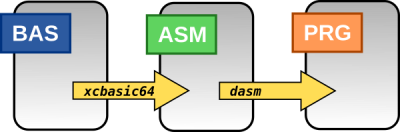
Before getting started, have a look at this figure to understand how XC=BASIC source files are compiled to C64 executable programs. There are two steps involved. First, the xcbasic64 compiler compiles the .bas source file to an intermediate assembly source. Then DASM is kicked in and it assembles the intermediate source file to program file.
Step 1: install DASM
- Go to this page and download the latest DASM release for your operating system.
- Extract the package to a location that you'll remember
- On Linux, you have to add the executable permission:
chmod +x dasm - Recommended: add the executable to the PATH environment variable to make it callable from anywhere. If you don't know how to do this, read one of these guides: Windows, Linux and macOS. On Linux, it's often easier to symlink to the executable in a standard bin directory, e.g /usr/bin.
Step 2: install xcbasic64
- Go to the releases page and download the latest xcbasic64 release for your operating system.
- Extract the package to a location that you'll remember
- On Linux, you have to add the executable permission:
chmod +x xcbasic64 - Recommended: add the executable to the PATH environment variable (see above).
Usage
You can now invoke xcbasic64 from the command line as follows:
xcbasic64 [-options] source.bas target.prg
The following command line options can be used:
-o or --output= | Output type. Possible values are: prg (default) or asm. If set to asm, DASM will not be invoked and the intermediate assembly source will be output. |
-d or --dasm= | Path to the DASM executable. Defaults to “dasm.exe” (Windows) or “dasm” (Linux/Mac). This is required only if DASM is not in the executable path or you want to override this value for some reason. |
-s or --symbol= | Symbol dump file name. This is passed to DASM as it is. It is useful for debugging your program |
-l or --list= | List file name. This is passed to DASM as it is. Also useful for debugging. |
-n or --noopt | Do NOT run the optimizer |
-h or --help | Display help |
Code editors and third party tools
Editors
These editors offer syntax highlighting and integrated compile/run commands for the latest version of XC=BASIC:
- Textadept extended with XC=BASIC language module by Csaba Fekete
- Micro used with xcbasic-config by Carlos Augusto Zayas Guggiari
The following ones also work but they're not actively maintained:
- XC=Edit by Oliver Hermanni, an IDE for XC=BASIC
- Visual Studio Code extended with XC=BASIC language support by Viza (abandoned, pre-1.0 syntax only)
Tools
- XCB by Michael Longval, a front end for XC=BASIC. In the style of TurboPascal 3.0.